AngleBetweenHelices: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery perrow=2 heights=250px widths= | <gallery perrow=2 heights=250px widths=191px> | ||
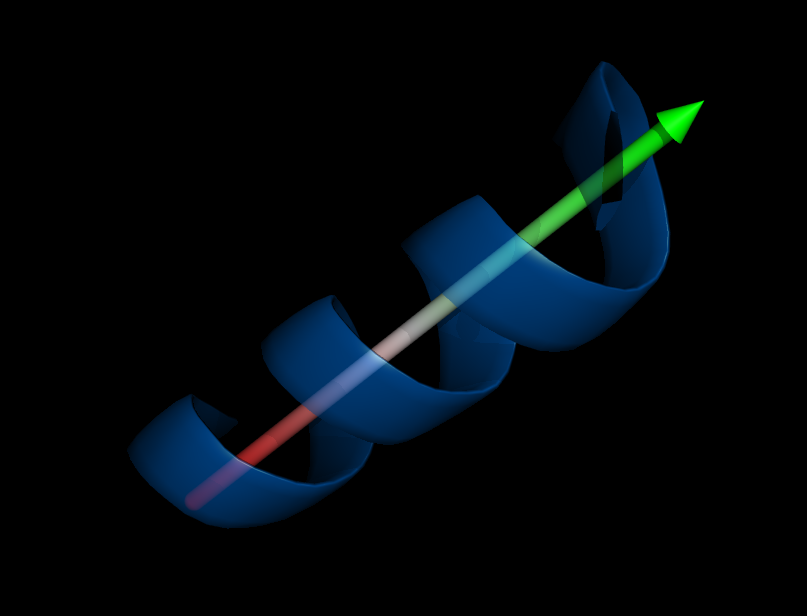
Image:Helix_orientation1.png|Orientation of a helix | Image:Helix_orientation1.png|Orientation of a helix | ||
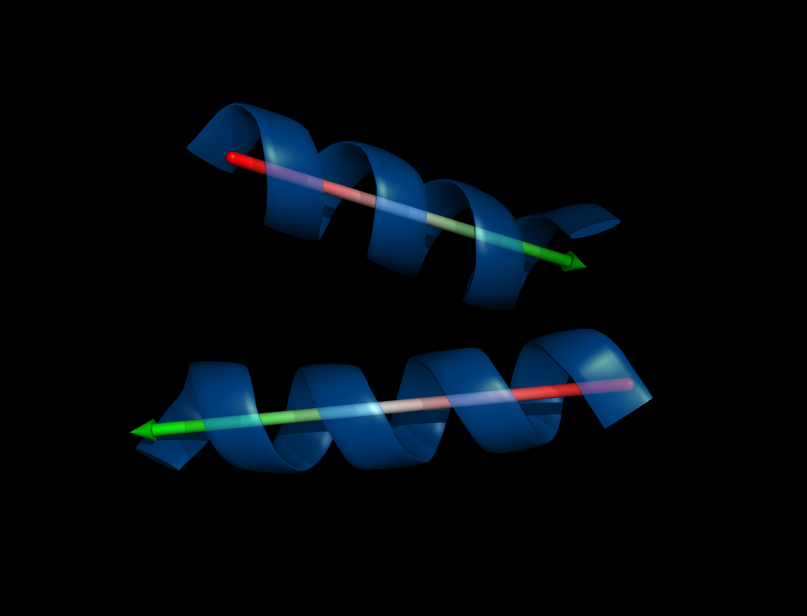
Image:Helix_orientation2.png|Orientation of two helices, their angle that separates the two is 145.08 degrees as reported by the script | Image:Helix_orientation2.png|Orientation of two helices, their angle that separates the two is 145.08 degrees as reported by the script | ||
Revision as of 08:29, 13 September 2010
Calculate angle between alpha-helices or beta-sheets. There are four different methods implemented to fit a helix, two of them also work for sheets or loops.
Commands
helix_orientation selection [, visualize [, sigma_cutoff [, quiet ]]]
helix_orientation_hbond selection [, visualize [, cutoff [, quiet ]]]
loop_orientation selection [, visualize [, quiet ]]
cafit_orientation selection [, visualize [, quiet ]]
angle_between_helices selection1, selection2 [, method [, visualize [, quiet ]]]
Example
fetch 2x19
select hel1, /2x19//B/23-36/
select hel2, /2x19//B/40-54/
# just calculate/visualize orientation of single alpha-helix
helix_orientation_hbond hel1
# get angle between two helices
angle_between_helices hel1, hel2
angle_between_helices hel1, hel2, method=1
angle_between_helices hel1, hel2, method=2
# get angle between beta-sheets
select sheet1, A/47-54/
select sheet6, A/146-149/
angle_between_helices sheet1, sheet6, method=loop_orientation
angle_between_helices sheet1, sheet6, method=cafit_orientation
Output:
PyMOL>angle_between_helices hel1, hel2, method=cafit_orientation
Using method: cafit_orientation
Angle: 145.08 deg
The Script
'''
(c) 2010 Thomas Holder
'''
from pymol import cmd, stored, CmdException
from chempy import cpv
import math
def _vec_sum(vec_list):
# this is the same as
# return numpy.array(vec_list).sum(0).tolist()
vec = cpv.get_null()
for x in vec_list:
vec = cpv.add(vec, x)
return vec
def _mean_and_std(x):
# this is the same as
# return (numpy.mean(x), numpy.std(x, ddof=1))
N = len(x)
if N < 2:
return (x[0], 0.0)
mu = sum(x)/float(N)
var = sum((i - mu)**2 for i in x) / float(N - 1)
return (mu, var**0.5)
def _common_orientation(selection, vec, visualize=1, quiet=0):
'''
Common part of different helix orientation functions. Does calculate
the center of mass and does the visual feedback.
'''
stored.x = []
cmd.iterate_state(-1, '(%s) and name CA' % (selection),
'stored.x.append([x,y,z])')
if len(stored.x) < 2:
print 'warning: count(CA) < 2'
raise CmdException
center = cpv.scale(_vec_sum(stored.x), 1./len(stored.x))
if visualize:
scale = cpv.distance(stored.x[0], stored.x[-1])
visualize_orientation(vec, center, scale, True)
cmd.zoom(selection, buffer=2)
if not quiet:
print 'Center: (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f) Direction: (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f)' % tuple(center + vec)
return center, vec
def visualize_orientation(direction, center=[0,0,0], scale=1.0, symmetric=False, color='green', color2='red'):
'''
Draw an arrow. Helper function for "helix_orientation" etc.
'''
from pymol import cgo
color_list = cmd.get_color_tuple(color)
color2_list = cmd.get_color_tuple(color2)
if symmetric:
scale *= 0.5
end = cpv.add(center, cpv.scale(direction, scale))
radius = 0.3
obj = [cgo.SAUSAGE]
obj.extend(center)
obj.extend(end)
obj.extend([
radius,
0.8, 0.8, 0.8,
])
obj.extend(color_list)
if symmetric:
start = cpv.sub(center, cpv.scale(direction, scale))
obj.append(cgo.SAUSAGE)
obj.extend(center)
obj.extend(start)
obj.extend([
radius,
0.8, 0.8, 0.8,
])
obj.extend(color2_list)
coneend = cpv.add(end, cpv.scale(direction, 4.0*radius))
obj.append(cgo.CONE)
obj.extend(end)
obj.extend(coneend)
obj.extend([
radius * 1.75,
0.0,
])
obj.extend(color_list * 2)
obj.extend([
1.0, 1.0, # Caps
])
cmd.load_cgo(obj, cmd.get_unused_name('oriVec'), zoom=0)
def cafit_orientation(selection, visualize=1, quiet=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Get the center and direction of a peptide by least squares
linear fit on CA atoms.
USAGE
cafit_orientation selection [, visualize]
NOTES
Requires python module "numpy".
SEE ALSO
helix_orientation
'''
visualize, quiet = int(visualize), int(quiet)
import numpy
stored.x = list()
cmd.iterate_state(-1, '(%s) and name CA' % (selection),
'stored.x.append([x,y,z])')
x = numpy.array(stored.x)
U,s,Vh = numpy.linalg.svd(x - x.mean(0))
vec = cpv.normalize(Vh[0])
if cpv.dot_product(vec, x[-1] - x[0]) < 0:
vec = cpv.negate(vec)
return _common_orientation(selection, vec, visualize, quiet)
def loop_orientation(selection, visualize=1, quiet=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Get the center and approximate direction of a peptide. Works for any
secondary structure.
Averages direction of N(i)->C(i) pseudo bonds.
USAGE
loop_orientation selection [, visualize]
SEE ALSO
helix_orientation
'''
visualize, quiet = int(visualize), int(quiet)
stored.x = dict()
cmd.iterate_state(-1, '(%s) and name N+C' % (selection),
'stored.x.setdefault(chain + resi, dict())[name] = x,y,z')
vec = cpv.get_null()
count = 0
for x in stored.x.itervalues():
if 'C' in x and 'N' in x:
vec = cpv.add(vec, cpv.sub(x['C'], x['N']))
count += 1
if count == 0:
print 'warning: count == 0'
raise CmdException
vec = cpv.normalize(vec)
return _common_orientation(selection, vec, visualize, quiet)
def helix_orientation(selection, visualize=1, sigma_cutoff=1.5, quiet=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Get the center and direction of a helix as vectors. Will only work
for helices and gives slightly different results than loop_orientation.
Averages direction of C(i)->O(i) bonds.
USAGE
helix_orientation selection [, visualize [, sigma_cutoff]]
ARGUMENTS
selection = string: atom selection of helix
visualize = 0 or 1: show fitted vector as arrow {default: 1}
sigma_cutoff = float: drop outliers outside
(standard_deviation * sigma_cutoff) {default: 1.5}
SEE ALSO
angle_between_helices, helix_orientation_hbond, loop_orientation, cafit_orientation
'''
visualize, quiet, sigma_cutoff = int(visualize), int(quiet), float(sigma_cutoff)
stored.x = dict()
cmd.iterate_state(-1, '(%s) and name C+O' % (selection),
'stored.x.setdefault(chain + resi, dict())[name] = x,y,z')
vec_list = []
count = 0
for x in stored.x.itervalues():
if 'C' in x and 'O' in x:
vec_list.append(cpv.sub(x['O'], x['C']))
count += 1
if count == 0:
print 'warning: count == 0'
raise CmdException
vec = _vec_sum(vec_list)
if count > 2 and sigma_cutoff > 0:
angle_list = [cpv.get_angle(vec, x) for x in vec_list]
angle_mu, angle_sigma = _mean_and_std(angle_list)
vec_list = [vec_list[i] for i in range(len(vec_list))
if abs(angle_list[i] - angle_mu) < angle_sigma * sigma_cutoff]
if not quiet:
print 'Dropping %d outlier(s)' % (len(angle_list) - len(vec_list))
vec = _vec_sum(vec_list)
vec = cpv.normalize(vec)
return _common_orientation(selection, vec, visualize, quiet)
def helix_orientation_hbond(selection, visualize=1, cutoff=3.5, quiet=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Get the center and direction of a helix as vectors. Will only work
for alpha helices and gives slightly different results than
helix_orientation. Averages direction of O(i)->N(i+4) hydrogen bonds.
USAGE
helix_orientation selection [, visualize [, cutoff]]
ARGUMENTS
cutoff = float: maximal hydrogen bond distance {default: 3.5}
SEE ALSO
helix_orientation
'''
visualize, quiet, cutoff = int(visualize), int(quiet), float(cutoff)
stored.x = dict()
cmd.iterate_state(-1, '(%s) and name N+O' % (selection),
'stored.x.setdefault(resv, dict())[name] = x,y,z')
vec_list = []
for resi in stored.x:
resi_other = resi + 4
if 'O' in stored.x[resi] and resi_other in stored.x:
if 'N' in stored.x[resi_other]:
vec = cpv.sub(stored.x[resi_other]['N'], stored.x[resi]['O'])
if cpv.length(vec) < cutoff:
vec_list.append(vec)
if len(vec_list) == 0:
print 'warning: count == 0'
raise CmdException
vec = _vec_sum(vec_list)
vec = cpv.normalize(vec)
return _common_orientation(selection, vec, visualize, quiet)
def angle_between_helices(selection1, selection2, method='helix_orientation', visualize=1, quiet=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Calculates the angle between two helices
USAGE
angle_between_helices selection1, selection2 [, method [, visualize]]
ARGUMENTS
selection1 = string: atom selection of first helix
selection2 = string: atom selection of second helix
method = string: function to calculate orientation {default: helix_orientation}
or int: 0: helix_orientation, 1: helix_orientation_hbond,
2: loop_orientation, 3: cafit_orientation
visualize = 0 or 1: show fitted vector as arrow {default: 1}
SEE ALSO
helix_orientation, helix_orientation_hbond, loop_orientation, cafit_orientation
'''
visualize, quiet = int(visualize), int(quiet)
methods = {
'0': helix_orientation,
'1': helix_orientation_hbond,
'2': loop_orientation,
'3': cafit_orientation,
}
methods.update((x.__name__, x) for x in methods.values())
try:
orientation = methods[str(method)]
except KeyError:
print 'no such method:', method
raise CmdException
if not quiet:
print 'Using method:', orientation.__name__
cen1, dir1 = orientation(selection1, visualize, quiet=1)
cen2, dir2 = orientation(selection2, visualize, quiet=1)
angle = cpv.get_angle(dir1, dir2)
angle_deg = math.degrees(angle)
if not quiet:
print 'Angle: %.2f deg' % (angle_deg)
if visualize:
cmd.zoom('(%s) or (%s)' % (selection1, selection2), buffer=2)
return angle_deg
cmd.extend('helix_orientation', helix_orientation)
cmd.extend('helix_orientation_hbond', helix_orientation_hbond)
cmd.extend('loop_orientation', loop_orientation)
cmd.extend('cafit_orientation', cafit_orientation)
cmd.extend('angle_between_helices', angle_between_helices)