Symexp
Symexp is used to reconstruct neighboring asymmetric units from the crystallographic experiment that produced the given structure. This is assuming the use of a PDB file or equivalent that contains enough information (CRYST1 record) to reproduce the lattice.
Symexp creates all symmetry related objects for the specified object that occurs within a cutoff about an atom selection. The new objects are labeled using the prefix provided along with their crystallographic symmetry operation and translation.
USAGE
# Expand the ''object'' around its ''selection'' by cutoff Angstroms and
# prefix the new objects withs ''prefix''.
symexp prefix, object, selection, cutoff [, segi]
For one protein:
symexp name_for_new_objects,asymmetric_name,(asymmetric_name),distance
ARGUMENTS
- prefix = string: name prefix for new objects
- object = string: name of the object that you wish to reproduce neighboring crystal partners for; the source of the symmetry operators
- selection = string: atom selection to measure cutoff distance from
- cutoff = float: create all symmetry mates that are within "cutoff" distance from selection
- segi = 0/1: if segi=1 then assign to each symmetry mate a unique 4-character segment identifier {default: 0}
EXAMPLE
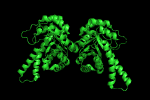
load any .pdb file into PyMOL (here we use 1GVF).
At the PyMOL command prompt type the following:
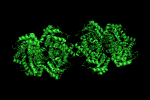
symexp sym,1GVF,(1GVF),1
produces three new objects. We now have four objects corresponding to two biologic units (the functional protein in a cell).
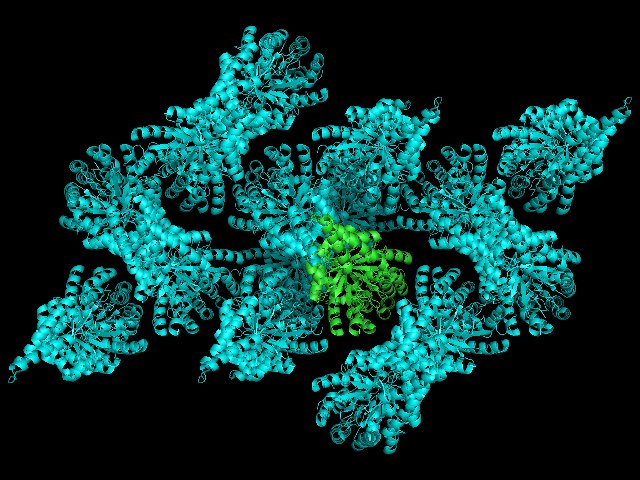
symexp sym,1GVF,(1GVF),5
If we color all of the sym* cyan we will produce the following:
As you can see, we can begin to understand the crystal environment of our asymmetric unit. Increasing distance will reveal more of the crystal lattice, but will place in increasing demand on your computer's rendering ability.
PyMOL is known to exit dramatically (crash) if you provide a scene that is too large or complex. This is a result of the low-level malloc function failing. See Category:Performance for workarounds.
See Also
- PDB Symmetry Info
- SuperSym
- Supercell
- From within PyMOL, help symexp and symexp ?.