Difference between revisions of "DynoPlot"
Cowsandmilk (talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| Line 211: | Line 211: | ||
# Reverse number by subtracting total number of pixels - value pixels | # Reverse number by subtracting total number of pixels - value pixels | ||
if axis == "Y": | if axis == "Y": | ||
| − | tot_label_diff = float(self.ylabels[ | + | tot_label_diff = float(self.ylabels[-1] - label0) |
tot_label_whole = int(tot_label_diff / inc) | tot_label_whole = int(tot_label_diff / inc) | ||
tot_label_part = float(float(tot_label_diff / inc) - tot_label_whole) | tot_label_part = float(float(tot_label_diff / inc) - tot_label_whole) | ||
Revision as of 06:30, 3 March 2010
DESCRIPTION
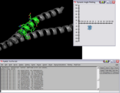
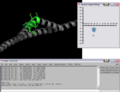
This script was setup to do generic plotting, that is given a set of data and axis labels it would create a plot. Initially, I had it setup to draw the plot directly in the PyMol window (allowing for both 2D and 3D style plots), but because I couldn't figure out how to billboard CGO objects (Warren told me at the time that it couldn't be done) I took a different approach. The plot now exists in it's own window and can only do 2D plots. It is however interactive. I only have here a Rama.(phi,psi) plot, but the code can be easily extended to other types of data. For instance, I had this working for an energy vs distance data that I had generated by another script.
This script will create a Phi vs Psi(Ramachandran) plot of the selection given. The plot will display data points which can be dragged around Phi,Psi space with the corresponding residue's Phi,Psi angles changing in the structure (PyMol window).
IMAGES
SETUP
place the DynoPlot.py script into the appropriate startup directory then restart PyMol
LINUX old-style installation
$PYMOL_PATH/modules/pmg_tk/startup/
LINUX distutils installation
/usr/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/pmg_tk/startup/
Windows
PYMOL_PATH/modules/pmg_tk/startup/ , where PYMOL_PATH on Windows is defaulted to C:/Program Files/DeLano Scientific/PyMol/start/
NOTES / STATUS
- Tested on Windows, PyMol version 0.97
- This is an initial version, which needs some work.
- Left, Right mouse buttons do different things; Right = identify data point, Left = drag data point around
- Post comments/questions or send them to: dwkulp@mail.med.upenn.edu
USAGE
rama SELECTION
EXAMPLES
- load pdb file 1ENV (download it or use the PDB loader plugin)
- select resi 129-136
- rama sel01
- rock # the object needs to be moving in order for the angles to be updated.
REFERENCES
SCRIPTS (DynoPlot.py)
DynoPlot.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
###############################################
# File: DynoPlot.py
# Author: Dan Kulp
# Creation Date: 8/29/05
#
# Notes:
# Draw plots that display interactive data.
# Phi,Psi plot shown.
###############################################
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import generators
import os,math
import Tkinter
from Tkinter import *
import Pmw
import distutils.spawn # used for find_executable
import random
from pymol import cmd
try:
import pymol
REAL_PYMOL = True
except ImportError:
print "Nope"
canvas = None
rootframe = None
init = 0
class SimplePlot(Tkinter.Canvas):
# Class variables
mark = 'Oval' # Only 'Oval' for now..
mark_size = 5
xlabels = [] # axis labels
ylabels = []
spacingx = 0 # spacing in x direction
spacingy = 0
xmin = 0 # min value from each axis
ymin = 0
lastx = 0 # previous x,y pos of mouse
lasty = 0
down = 0 # flag for mouse pressed
item = (0,) # items array used for clickable events
shapes = {} # store plot data, x,y etc..
def axis(self,xmin=40,xmax=300,ymin=10,ymax=290,xint=290,yint=40,xlabels=[],ylabels=[]):
# Store variables in self object
self.xlabels = xlabels
self.ylabels = ylabels
self.spacingx = (xmax-xmin) / (len(xlabels) - 1)
self.spacingy = (ymax-ymin) / (len(ylabels) - 1)
self.xmin = xmin
self.ymin = ymin
# Create axis lines
self.create_line((xmin,xint,xmax,xint),fill="black",width=3)
self.create_line((yint,ymin,yint,ymax),fill="black",width=3)
# Create tick marks and labels
nextspot = xmin
for label in xlabels:
self.create_line((nextspot, xint+5,nextspot, xint-5),fill="black",width=2)
self.create_text(nextspot, xint-15, text=label)
if len(xlabels) == 1:
nextspot = xmax
else:
nextspot += (xmax - xmin)/ (len(xlabels) - 1)
nextspot = ymax
for label in ylabels:
self.create_line((yint+5,nextspot,yint-5,nextspot),fill="black",width=2)
self.create_text(yint-20,nextspot,text=label)
if len(ylabels) == 1:
nextspot = ymin
else:
nextspot -= (ymax - ymin)/ (len(ylabels) - 1)
# Plot a point
def plot(self,xp,yp,meta):
# Convert from 'label' space to 'pixel' space
x = self.convertToPixel("X",xp)
y = self.convertToPixel("Y",yp)
if self.mark == "Oval":
oval = self.create_oval(x-self.mark_size,y-self.mark_size,x+self.mark_size,y+self.mark_size,width=1,outline="black",fill="SkyBlue2")
self.shapes[oval] = [x,y,0,xp,yp,meta]
# Repaint all points
def repaint(self):
for value in self.shapes.values():
x = value[0]
y = value[1]
self.create_oval(x-self.mark_size,y-self.mark_size,x+self.mark_size,y+self.mark_size,width=1,outline="black",fill="SkyBlue2")
# Convert from pixel space to label space
def convertToLabel(self,axis, value):
# Defaultly use X-axis info
label0 = self.xlabels[0]
label1 = self.xlabels[1]
spacing = self.spacingx
min = self.xmin
# Set info for Y-axis use
if axis == "Y":
label0 = self.ylabels[0]
label1 = self.ylabels[1]
spacing = self.spacingy
min = self.ymin
pixel = value - min
label = pixel / spacing
label = label0 + label * abs(label1 - label0)
if axis == "Y":
label = - label
return label
# Converts value from 'label' space to 'pixel' space
def convertToPixel(self,axis, value):
# Defaultly use X-axis info
label0 = self.xlabels[0]
label1 = self.xlabels[1]
spacing = self.spacingx
min = self.xmin
# Set info for Y-axis use
if axis == "Y":
label0 = self.ylabels[0]
label1 = self.ylabels[1]
spacing = self.spacingy
min = self.ymin
# Get axis increment in 'label' space
inc = abs(label1 - label0)
# 'Label' difference from value and smallest label (label0)
diff = float(value - label0)
# Get whole number in 'label' space
whole = int(diff / inc)
# Get fraction number in 'label' space
part = float(float(diff/inc) - whole)
# Return 'pixel' position value
pixel = whole * spacing + part * spacing
# print "Pixel: %f * %f + %f * %f = %f" % (whole, spacing, part, spacing,pixel)
# Reverse number by subtracting total number of pixels - value pixels
if axis == "Y":
tot_label_diff = float(self.ylabels[-1] - label0)
tot_label_whole = int(tot_label_diff / inc)
tot_label_part = float(float(tot_label_diff / inc) - tot_label_whole)
tot_label_pix = tot_label_whole * spacing + tot_label_part *spacing
pixel = tot_label_pix - pixel
# Add min edge pixels
pixel = pixel + min
return pixel
# Print out which data point you just clicked on..
def pickWhich(self,event):
# Find closest data point
x = event.widget.canvasx(event.x)
y = event.widget.canvasx(event.y)
spot = event.widget.find_closest(x,y)
# Print the shape's meta information corresponding with the shape that was picked
if spot[0] in self.shapes:
print "Residue(Ca): %s\n" % self.shapes[spot[0]][5][2]
# Mouse Down Event
def down(self,event):
# Store x,y position
self.lastx = event.x
self.lasty = event.y
# Find the currently selected item
x = event.widget.canvasx(event.x)
y = event.widget.canvasx(event.y)
self.item = event.widget.find_closest(x,y)
# Identify that the mouse is down
self.down = 1
# Mouse Up Event
def up(self,event):
# Get label space version of x,y
labelx = self.convertToLabel("X",event.x)
labely = self.convertToLabel("Y",event.y)
# Convert new position into label space..
if self.item[0] in self.shapes:
self.shapes[self.item[0]][0] = event.x
self.shapes[self.item[0]][1] = event.y
self.shapes[self.item[0]][2] = 1
self.shapes[self.item[0]][3] = labelx
self.shapes[self.item[0]][4] = labely
# Reset Flags
self.item = (0,)
self.down = 0
# Mouse Drag(Move) Event
def drag(self,event):
# Check that mouse is down and item clicked is a valid data point
if self.down and self.item[0] in self.shapes:
self.move(self.item, event.x - self.lastx, event.y - self.lasty)
self.lastx = event.x
self.lasty = event.y
def __init__(self):
self.menuBar.addcascademenu('Plugin', 'PlotTools', 'Plot Tools',
label='Plot Tools')
self.menuBar.addmenuitem('PlotTools', 'command',
'Launch Rama Plot',
label='Rama Plot',
command = lambda s=self: ramaplot())
def ramaplot(x=0,y=0,meta=[],clear=0):
global canvas
global rootframe
global init
# If no window is open
if init == 0:
rootframe=Tk()
rootframe.title(' Dynamic Angle Plotting ')
rootframe.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", close_callback)
canvas = SimplePlot(rootframe,width=320,height=320)
canvas.bind("<Button-2>",canvas.pickWhich)
canvas.bind("<Button-3>",canvas.pickWhich)
canvas.bind("<ButtonPress-1>",canvas.down)
canvas.bind("<ButtonRelease-1>",canvas.up)
canvas.bind("<Motion>",canvas.drag)
canvas.pack(side=Tkinter.LEFT,fill="both",expand=1)
canvas.axis(xint=150,xlabels=[-180,-150,-120,-90,-60,-30,0,30,60,90,120,150,180],ylabels=[-180,-150,-120,-90,-60,-30,0,30,60,90,120,150,180])
canvas.update()
init = 1
else:
canvas.plot(int(x), int(y),meta)
def close_callback():
global init
global rootframe
init = 0
rootframe.destroy()
# New Callback object, so that we can update the structure when phi,psi points are moved.
class DynoRamaObject:
global canvas
def start(self,sel):
# Get selection model
model = cmd.get_model(sel)
residues = ['dummy']
resnames = ['dummy']
phi = []
psi = []
dummy = []
i = 0
# Loop through each atom
for at in model.atom:
# Only plot once per residue
if at.chain+":"+at.resn+":"+at.resi not in residues:
residues.append(at.chain+":"+at.resn+":"+at.resi)
resnames.append(at.resn+at.resi)
dummy.append(i)
i += 1
# Check for a null chain id (some PDBs contain this)
unit_select = ""
if at.chain != "":
unit_select = "chain "+str(at.chain)+" and "
# Define selections for residue i-1, i and i+1
residue_def = unit_select+'resi '+str(at.resi)
residue_def_prev = unit_select+'resi '+str(int(at.resi)-1)
residue_def_next = unit_select+'resi '+str(int(at.resi)+1)
try:
# Store phi,psi residue definitions to pass on to plot routine
phi_psi = [
# Phi angles
residue_def_prev+' and name C',
residue_def+' and name N',
residue_def+' and name CA',
residue_def+' and name C',
# Psi angles
residue_def+' and name N',
residue_def+' and name CA',
residue_def+' and name C',
residue_def_next+' and name N']
# Compute phi/psi angle
phi = cmd.get_dihedral(phi_psi[0],phi_psi[1],phi_psi[2],phi_psi[3])
psi = cmd.get_dihedral(phi_psi[4],phi_psi[5],phi_psi[6],phi_psi[7])
print "Plotting Phi,Psi: "+str(phi)+","+str(psi)
ramaplot(phi,psi,meta=phi_psi)
except:
continue
def __call__(self):
# Loop through each item on plot to see if updated
for key,value in canvas.shapes.items():
dihedrals = value[5]
# Look for update flag...
if value[2]:
# Set residue's phi,psi to new values
print "Re-setting Phi,Psi: %s,%s" % (value[3],value[4])
cmd.set_dihedral(dihedrals[0],dihedrals[1],dihedrals[2],dihedrals[3],value[3])
cmd.set_dihedral(dihedrals[4],dihedrals[5],dihedrals[6],dihedrals[7],value[4])
value[2] = 0
# The wrapper function, used to create the Ploting window and the PyMol callback object
def rama(sel):
rama = DynoRamaObject()
rama.start(sel)
cmd.load_callback(rama, "DynoRamaObject")
cmd.zoom("all")
# Extend these commands
cmd.extend('rama',rama)
cmd.extend('ramaplot',ramaplot)